Information technology (IT) infrastructure is the basic building block one needs to operate and handle enterprise IT environments. One can deploy it within an organization’s facilities or a cloud computing system.
IT infrastructure embraces various components like hardware, software, OS, network, and data storage (we will discuss later in this post) used to deliver the best IT services and solutions. You will find IT infrastructure products as downloadable software apps that run on top of current IT resources, like Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS).
Today, in this post, we will talk about IT infrastructure, its types, components, management, and a lot more.
Let’s start!
What Is IT Infrastructure?
Let’s check out the easy definition of IT infrastructure.
IT infrastructure is the collection of software, hardware, network systems, frameworks, and facilities that deliver IT services to distinct business units. Moreover, it assists in managing its digital presence.
In other words, it is broadly defined as a set of IT components that are the basis of an IT service, typically the physical components, many software, and network components.
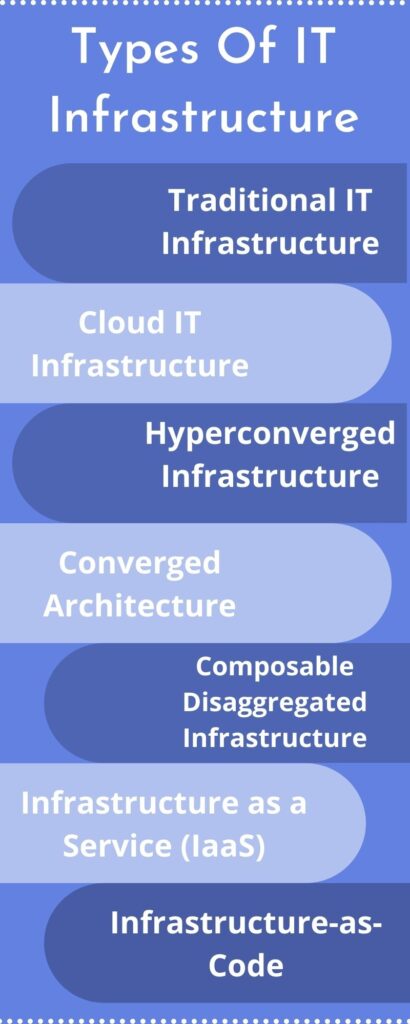
Types Of IT Infrastructure
An Information Technology architecture describes how you craft and structure your IT components for simpler management, better performance, cost-efficiency, and scalability.
Various types of IT infrastructure architectures are there you can choose from, as per the nature and size of your organization.
Let’s check out the types of IT infrastructure below:
1. Traditional IT Infrastructure
It usually includes hardware and software components, such as desktop computers, servers, enterprise software solutions, etc. Servers run and are installed typically on-premises to offer employees access to the needed apps and information.
The development team demands more space and strength to integrate traditional infrastructure. In many cases, traditional IT infrastructure is quite expensive when it comes to setup and support. One needs to purchase costly equipment and allocate the resources for maintenance. Moreover, the system demands frequent upgradation to scale up data storage or other services that help support more users.
Traditional IT infrastructure leads to the most secure data hosting solution. Besides, it provides complete control over your organization’s data and app.
2. Cloud IT Infrastructure
It’s pretty popular because of its convenience. In the cloud, despite any physical hardware, all software, servers, and networks are hosted.
So, instead of spending an amount on purchasing physical servers in-house, one can take data storage on rent from cloud computing providers, such as Amazon.
Characteristics of Cloud-Based Apps
In a cloud infrastructure, the app’s data is stored. So, there’s a minimum need for devices to run the app.
- Customers are capable of using the application from any device. The complete information is stored in the cloud. So, users can work on any device.
- One can store data on the device. Moreover, it permits the app to perform offline. Although, once the device comes online again, the application updates automatically. Resultantly, the entire information gets updated to the cloud.
3. Hyperconverged Infrastructure
It’s similar to a converged IT infrastructure (we will cover it next). It breaks silos and facilitates a centralized system. Moreover, it makes the use of software components hosted on a hypervisor for succeeding. Its key components are software-defined storage, the hypervisor, and software-defined networking. Furthermore, it allows resource federation across the processes. Usually, this sort of IT infrastructure architecture operates using commercial off-the-rack (COTS) servers.
4. Converged Architecture
This IT infrastructure architecture locates the fragmentation of traditional infrastructure. It groups the relevant IT components into a single and optimized hub. Next, it sets up the connected workflows for centralized visibility. Furthermore, it groups the available resources into “resource pools” that different apps and processes share according to the business policies and priorities. The cloud further makes converged IT infrastructure architectures easier to centralize, consolidate, and distribute resources.
5. Composable Disaggregated Infrastructure
It’s a sub-type of converged architecture and uses on-premises IT components. It’s powered by high-speed, low-latency networks, which permit quick resource allocation and minimum downtimes. Besides, it is the latest technology that’s surfacing, allowing physical data centers to act like virtual servers to allocate resources on-demand. Also, it is known as an emerging alternative for digital-native enterprises.
6. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
It’s a service provider that manages the business infrastructure, network, servers, storage, and visualization through a private or public cloud. Being a business owner, you can access the infrastructure using an admin panel or an API. Furthermore, you can handle OSs and apps while providers (such as Microsoft Azure or AWS) offer you networking, hardware, storage, hard drives, and servers.
IaaS has various advantages
- Usage-Based Cost
- Reduced Capital Expenditure
- Increased Security
- Easy Access
7. Infrastructure-as-Code
A specific IT infrastructure management strategy that allows maintenance and management of the architecture using lines of code or software apps instead of UI settings or physical hardware configuration is IaaC. Infrastructure as a code applies to software and hardware, both the IT components, with the strategically deployed code that assists in availing resources, monitoring processes, implementing security, and conducting other activities.
What Are The IT Infrastructure Components?
IT infrastructure components are a combination of software, hardware, and networks. The system’s design helps to improve communication between components, linking desktops to networks, devices to printers, and servers to the cloud.
There are various ways to organize, deploy, and integrate IT infrastructure components.
Let’s find the components of typical IT infrastructure.
1. Hardware
It refers to the IT infrastructure’s physical components that can be a cluster of devices from PCs to servers:
- Personal Computers ( laptops or desktops)
- Servers
- Mobile Devices (including tablets)
- Hubs
- Data Centers
- Routers
- Switches
2. Software
The apps that companies use for internal purposes to offer services to customers are software. An OS, such as macOS, is an integral part of the software. Moreover, the operating system is liable for handling hardware and system resources:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
- Content Management Systems (CMS)
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Web Servers
- Operating Systems
- Any Other Apps
3. Network
Networking facilitates connectivity between all devices and elements to ensure firewall, internet connectivity, and security:
- Data Centers
- Servers
- Routers
- Hubs
- Switches
What Is IT Infrastructure Management?
IT infrastructure management is the coordination of IT systems, resources, people, platforms, and environments. Following are some most common types of technology infrastructure management:
1. IT Operational Management Or ITOM
It refers to the bunch of processes and tools that assist in maintaining IT infrastructure. The practice also ensures that the picked IT infrastructure is reliable, available, and effective as a part of the business.
ITOM holds many functions, such as operational intelligence and data collection, network asset discovery, orchestration, cloud management, and network event management.
2. IT Asset Management Or ITAM
It’s responsible for IT infrastructure’s lifecycle management, both software, and hardware. Usually, it includes three parts:
- Financial
The main target of ITAM is to optimize IT expenses, which states implementing cost-effective IT infrastructure, ensuring that the new investments are demanded and cost-justified.
- Contractual
The managers handle cloud service agreements, software license agreements, and other contracts relevant to IT infrastructure.
- Inventory
It states that the managers control the issues of IT infrastructure. Resultantly, it becomes possible to make sensible decisions when investing in IT infrastructure.
3. IT Service Management Or ITSM
It refers to entire activities included in creating, designing, supporting, delivering, and managing IT services’ lifecycle.
IT service management targets facilitating and maintaining optimal deployment, management, operation of all IT resources for all the users in the extended enterprise.
4. OS Management
It helps handle environments driving the same operating system by offering patches, content, subscription management, and provisioning.
5. Virtualization Management
It interfaces with the virtual environments and the underlying physical hardware to ease resource administration, streamline operations, and improve data analysis.
6. Cloud Management
The cloud admins control everything running in a cloud, such as apps, data, end-users, and services, by handling resource deployments, disaster recovery, integration, and use.
7. IT Automation
Also known as infrastructure automation, it crafts repeatable processes and instructions to reduce and replace human interaction with IT systems.
8. Configuration Management
It helps maintain servers, computer systems, and software in a consistent desired state. Moreover, it tracks individual configuration products of an IT system.
9. Risk Management
It assists in identifying and assessing the risks and crafts plans to control or reduce those risks and their potential effects.
10. API Management
It is best at distributing, controlling, and analyzing the application programming interfaces (APIs) that help connect apps and data across clouds and enterprises.
Conclusion
We hope this post has cleared all your confusion and helped you understand IT infrastructure and related topics.
Before investing in IT infrastructure, you need to understand everything about it, its components, management, types, and more.





 USA
USA UK
UK